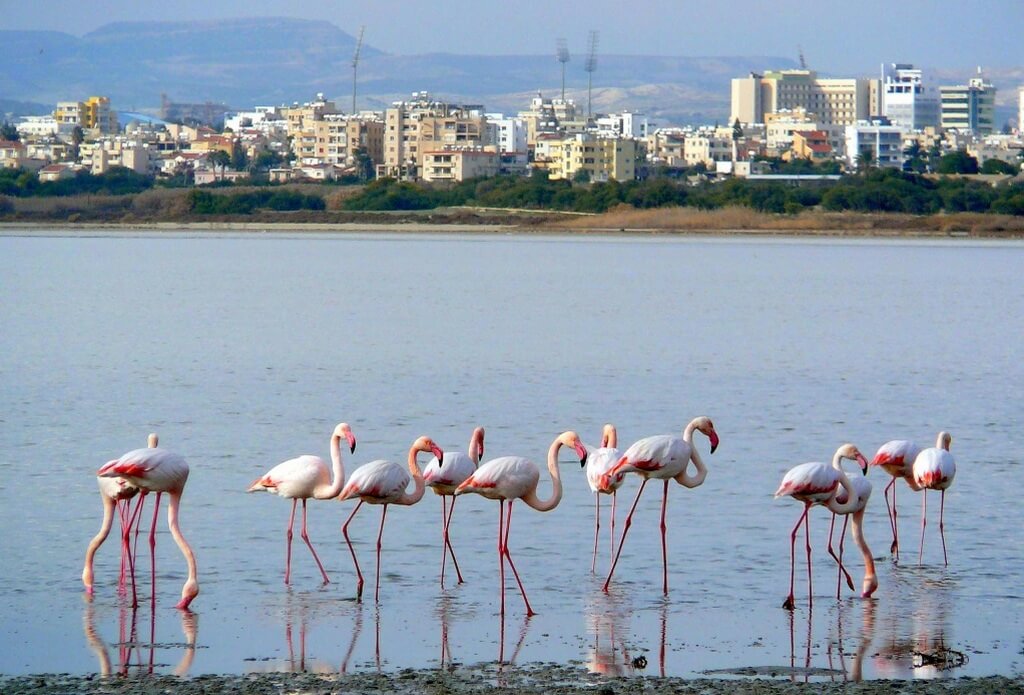
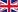
Larnaka Salt Lake is the second largest salt-lake in Cyprus and measures 2.2 square kilometres. In 1997 it was declared a protected area under Cypriot Law for the Protection and Management of Nature and Wildlife and under the European Habitats Directive.
It is a significant Ramsar and Natura 2000 site – one of the most significant biotopes in Europe - and one of the most important habitats in Europe for waterfowl.
Located southwest of Larnaka town and east of the villages of Meneou and Dromolaxia, the Salt Lake – known locally as ‘Alyki’ - is actually one of four lakes in Larnaka. Together, with Lake Orphani, Lake Soros and Airport Lake, the lakes collectively cover a total area of 1761 hectares.
During the winter, the lake fills with water and is home to migrating birds, including thousands of flamingos that stay between November and March, along with wild ducks and other water or shore fowl that find refuge here on their migratory journeys. The most basic element of the food chain in the lakes’ ecosystem is the small brine shrimp Artemia (Artemia salina), which the other life greatly relies on. When flamingos and other water birds are unable to find the shrimp, they desert the salt lakes and continue their journey by travelling to Lake Akrotiri in Lemesos or south towards Africa.
Archaeological finds show that the Salt Lake area and that of the nearby mosque have been inhabited since the Late Bronze Age (2nd century BC). In prehistoric times the Salt Lake was a harbour that served the town, unearthed near where the Hala Sultan Tekkesi mosque stands today. The town was one of the large urban and commercial centres of Cyprus in the Late Bronze Age (1650-1050BC). When the town was abandoned, the estuary silted up and the natural harbour was destroyed.
According to legend, the lake's saltiness stems from Agios Lazaros (Saint Lazarus) request of an old woman for food and drink. She refused, claiming her vines had dried up, to which Lazarus replied ‘may your vines be dry and be a salt lake forever more’. A more scientific explanation is that the salt water penetrates the porous rock between the lake and the sea, making the water very salty.
Winding through the lake area is a designated, linear nature trail that is 4 km in length, and leads all the way up to the old aqueduct of Kamares. The various flora of trees, shrubs and flowers is signposted with information along the way, and there are also periodic benches, making the path popular for walkers and joggers.
Throughout the Middle Ages, salt was so plentiful that it became one of the primary export commodities of Cyprus. Its harvesting and selling were strictly controlled and taxed. Salt was last harvested in 1986.